Suction Foundation
Seawalls, such as breakwaters and quays, are massive structures that need strong base to support the huge weight.
A conventional method of constructing a foundation with tens to hundreds kg of stones (rubble mound) has caused to increase the construction cost as a larger rubble mound is needed along with a trend in which the structures are commonly constructed at deeper water area.
At a seabed in very bad soil condition, another labors are needed, including seabed excavation and replacement (replacing with better soil).
For this solution, aiming at more saving of construction cost, we developed a suction foundation as a new base that supports a huge port structure.
This suction foundation is a base structure in shape of an upside-down teacup. The foundation unit is directly embedded onto the seabed. It is therefore considered that it has a high stability
Features of Suction Foundation

- No need of rubble-mound, seabed excavation, and replacement leads to reduce the structural cross-section and also construction period.
- No need of specific construction machine. It can be constructed at least with drainage pumps to increase the suction power and crane ships for installation in good arrangement.
- The frictional force of the bottom soil in the foundation unit embedded unto the seabed and the soil pressure at the back wall turn a sufficient resistant force to withstand against sliding.
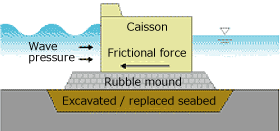
Composite breakwater (conventional type)
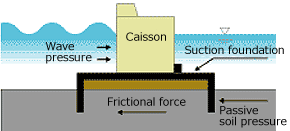
Suction foundation breakwater
Development period
- FY1997 to FY2001
Submerging of Suction Foundation
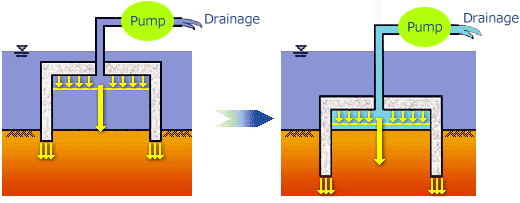
The suction foundation is mounted on the seabed soil facing the aperture
of the foundation unit downward.
When the inside of the foundation unit is sealed by the seabed surface,
the inside water is drained forcibly using a pump, resulting in difference
of hydraulic pressure between inside and outside of the foundation unit.
The suction force generated by the difference of hydraulic pressure is
used as a press force to submerge the foundation unit onto the seabed soil.
Applied structure

Example of applications: Quay (Integrated unit of suction foundation and upper caisson)
- Foundation of breakwater; Mound less breakwater
- Foundation of quay and shore protection; Reinforced quay against earthquakes
- Moored buoy; Suction anchor
- Foundation of floating structure; Foot protection to prevent scouring
